An In-depth Look How Solar Powered Lighting Systems Function
Solar lighting systems usually generate and store their own power during the day and release it at night. A couple of years back, the thought of harnessing the power of the sun would have seemed ridiculous. Now, you will notice many solar panels on the rooftops of buildings and on streetlights in the cities. This has been made possible by companies such as enkonn lighting which ensure that they offer us more sustainable lighting solutions.

Enkonn Lighting
How do solar lighting systems work?
How exactly do the solar panels convert sunlight into power that is used to light up bulbs? The way that these bulbs work is extremely interesting. The solar lighting systems work through the photovoltaic (PV) effect. The PV effect enables the solar panels to generate energy that is stored in the batteries.
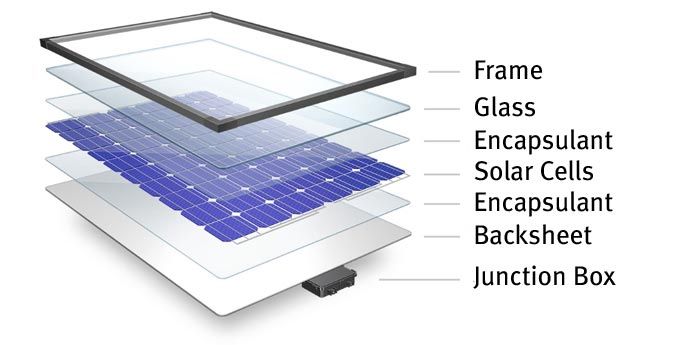
Basically, a solar powered light has 4 major components:
- A solar panel also called a solar cell
- A battery
- Control electronics
- The light fixture

Enkonn Lighting
When there is sunlight, the solar panel produces power to charge the battery. This is made possible by the photons that are produced during the day by the sun. These photons stimulate electron production in the silicon cells; the electrons are knocked off and move from the panel into the battery where they’re stored.
The entire process described above takes place during the day from sunrise to sunset.
The control electronics are some sort of sensors that notice when it starts getting dark. They can determine this from the fact that as night approaches, there is reduced production of power. When the battery stops being fed, it triggers the light fixture to turn on.
The light operates on the set schedule; from dusk till dawn.
When the battery becomes too low or empty, the control electronics detect the changes and cause power to be produced by the solar panel again.
Additional points…
The panel consists of several layers. The front layer has a chemical that creates negatively charged electrons when the sun’s rays go through it. The electrons that are created create an excitation and pass to the back layer.

Enkonn Lighting
The back has crystalline silicone and a chemical that generates positively charged spaces. These spaces conduct the solar power through the wires that are embedded within the panel. This transmission is essentially what makes up the photovoltaic effect.
The solar panel can produce approximately 0.45 volts. This, however, is dependent on the amount of sunlight that hits the surface of the panel and the size.
If you are using more than one cell, it is advisable to arrange them in series rather than in parallel. For example, if four 0.45-volts cells are arranged in series, they will produce a total of 1.8 volts.
The solar panel is connected to the rechargeable battery using a diode. The purpose of this is to prevent current from flowing from the battery to the solar panel at night.
This process repeats itself on a daily cycle. Once the battery is depleted after using it overnight, it recharges throughout the day in preparation for the following night.